What is a Product Code? A Simple Guide for Businesses
Product codes span every corner of commerce, from the barcode scanned at checkout to the RFID tag tracking shipments across continents. They help businesses precisely identify products. Whether you are a startup, retailer, or manufacturer, understanding these codes is essential to running a smarter, more efficient business.
This article will explore types of these codes, explore how they’re carried, and show you how to verify them using trusted tools.
Table of Contents
What is a product code?
A product code is a unique identifier assigned to a specific product type or variant. It helps distinguish one branded product from another across systems, platforms, and markets. These codes are typically used in supply chain and inventory management to track, store, and move products accurately.
These codes enable businesses to identify products, track stock levels, streamline supply chains, and ensure accurate pricing and product listings.
To make these codes usable across industries, they are most commonly embedded in barcodes. Barcodes are visual, machine-readable images that represent these codes in a format that scanners can quickly interpret.
You may usually encounter these codes in everyday scenarios, like when a barcode scanner doesn’t work at checkout and the cashier enters the code manually, or in e-commerce, people often use these codes to compare prices across websites
These codes serve three key purposes:
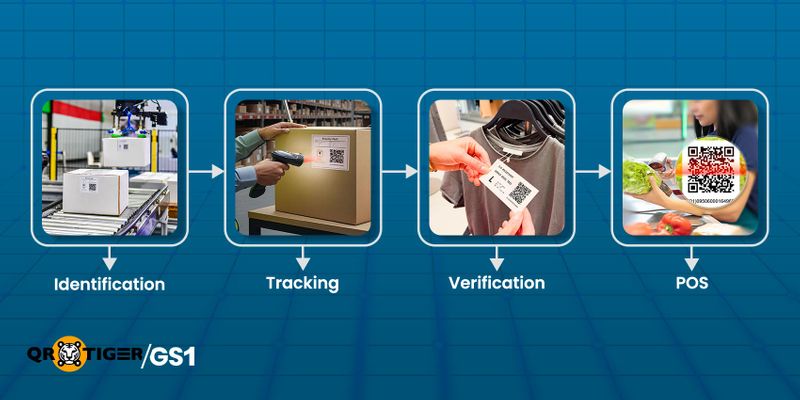
- Identification: They help businesses and systems identify and differentiate products, even those with identical names or packaging.
- Tracking: The codes enable effective inventory management, shipment tracking, and product lifecycle monitoring (from manufacturing to sale).
- Sales: When used at checkout, these codes (often embedded in barcodes) facilitate quick, precise scanning and show pricing details.
Common types include GTIN (Global Trade Item Number), and SKU (Stock Keeping Unit).
- GTIN is a standardized identifier developed by GS1. It is used globally across supply chains, retail systems, and e-commerce platforms to uniquely identify trade items such as products or services. GTINs are embedded in barcodes and are essential for interoperability between systems, facilitating smooth product recognition across retailers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- SKU is an internal, company-specific identifier used for inventory management. SKUs are highly flexible and customizable, allowing businesses to encode product attributes like color, size, or variant in a format that suits their operational needs.
- Other types that are less prevalent are ASIN (Amazon Standard Identification Number), MPN (Manufacturer Part Numbers), ISBN for books, and VIN for vehicles.
Types of GTIN product codes

GTIN 12
A UPC is a 12-digit numeric code used primarily in the U.S. and Canada to identify retail products. It’s encoded in a barcode and scanned at the point of sale (POS). The structure includes a manufacturer prefix, item reference, and a check digit. UPCs are issued by GS1 US.
GTIN 13
The EAN, now part of the GTIN system, is a 13-digit code used internationally. It is also known as the International Article Number.
It is used for uniquely identifying products in global trade. It helps manufacturers, retailers, and warehouses manage products efficiently by providing a unique identifier in the supply chain. EAN-13 format includes a country code, company prefix, item reference, manufacturer code, and check digit.
GTIN 8
GTIN-8 is a shorter, 8-digit product identifier used when standard UPC or EAN-13 barcodes won’t fit on the packaging. It’s encoded using the EAN-8 format and is meant for very small retail items.
Unlike GTIN-13, GTIN-8s are not created using a company prefix. They must be requested from your local GS1 office and are issued individually.
The following table compares different types of product codes.
| Code type | Structure and format | Primary use | Barcode symbol |
| GTIN 12 | 12-digit numeric code | (Manufacturer or company prefix, item ref, check digit) | Retail product identification primarily in the U.S. and Canada | UPC |
| GTIN 13 | 13-digit numeric code | (Similar to GTIN 12 but has a country code added) | Global product identification and trade | EAN 13 |
| GTIN 8 | 8-digit numeric code| (smaller version of the GTIN 13) | Small items with space limits | EAN 8 |
Product code carriers
They are the physical or digital mediums that store encoded product information. They facilitate automated identification, tracking, and data capture across supply chains. The most common types are discussed below.
Barcode symbologies
Barcodes are the most widely used product code carriers. They encode data in visual patterns that can be scanned and interpreted by machines.
- 1D (one-dimensional) barcodes are commonly seen as parallel black-and-white lines in retail environments. 1D barcodes are seen on products that a cashier scans at point of sale checkout.
- 2D (two-dimensional) barcodes appear as pixelated squares capable of storing more complex data. The common types include QR codes and DataMatrix.
A 2D barcode that stores data vertically and horizontally. It can encode more information than a traditional linear, 1D barcode.
The GS1 Digital Link QR code is an advanced 2D barcode following the GS1 standards, a global organization that provides universally recognized barcodes. These versatile barcodes simplify product traceability and consumer engagement by connecting to digital content and additional data.
Sunrise 2027 is a global initiative encouraging retailers to incorporate 2D barcodes (such as Data Matrix and GS1 QR codes) into their point of sale (POS) and supply chain systems by 2027.
The shift to 2D barcodes is optional, not mandatory. Traditional 1D barcodes will still be accepted and supported.
However, certain industries or government regulations may require businesses to adopt 2D barcodes for specific use cases. It's important to check if your sector has such requirements.
For example, the EU’s Digital Product Passport (DPP) initiative is one situation where these codes become necessary to meet compliance standards.
During the transition phase, both the 1D and 2D barcodes must be present on the packaging to help maintain compatibility with retailers whose systems and devices are not 2D barcode compatible.
GS1 does not provide QR code generation. Instead, companies can develop their own software for generating GS1 2D barcodes (by following GS1’s implementation guidelines). Alternatively, companies can use a third-party service like the GS1 QR code generator by QR Tiger.
By using a GS1 QR code for detailed product information, businesses can enhance traceability, optimize recall management, and enable dynamic pricing. These codes also let businesses benefit their consumers with greater transparency into allergens, product sustainability data, and certifications.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)
RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Note that RFID systems should comply with international standards like ISO/IEC 17360:2023 for traceability and interoperability.
The read range varies from a few centimetres to several meters. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags can be read through packaging or materials. Line-of-sight is not required.
Why are product code and their carriers important?
These codes and the carriers that deliver them are foundation in modern business operations. From inventory control to maintaining regulatory compliance, they ensure that products are accurately identified, tracked, and managed across the entire supply chain. Let’s understand the reasons behind their importance.
Accurate product identification
These codes and carriers allow businesses to precisely distinguish products, even among thousands of items. This ensures consistency across systems, from manufacturing to retail, decreasing errors and enhancing operational efficiency.
Efficient inventory and supply chain management
These codes allow real-time tracking of goods, helping businesses manage reordering, monitor stock levels, and reduce waste.
Barcode and RFID carriers automate data capture, optimizing warehouse operations and minimizing manual entry errors.
Interoperability in global trade compliance
Standardized codes like EAN ensure products are recognized across borders, enabling international commerce. They support interoperability between logistics providers, trading partners, and regulatory bodies.
Data accuracy for efficient operations
Scanning barcodes or RFID tags is faster and more accurate than manual data entry, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency.
Through product carriers, these codes integrate effectively with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and POS systems, facilitating automated workflows and data analytics.
How to Look Up or Verify a GTIN Product Code
It is essential to verify these codes for retrieving product details, validating authenticity, and ensuring accurate listings. The following methods discuss how to do it:
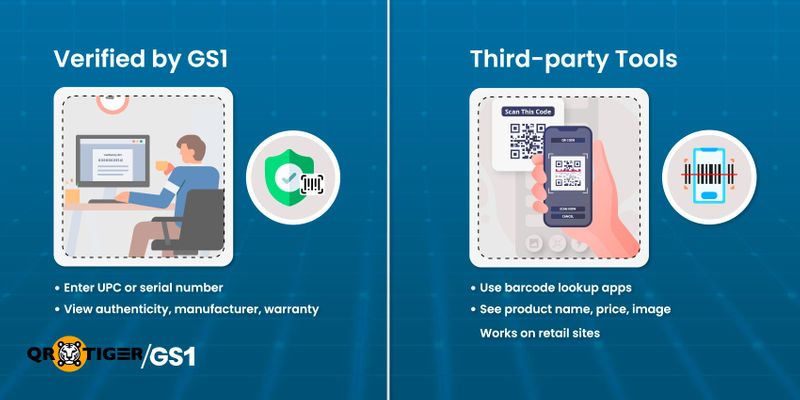
Using Verified by GS1
Many manufacturers offer online tools to check product details. Users can enter a serial number, a model number, or a UPC on official sites to find out if a product is real and check its specs or warranty.
The GS1 Company Prefix in a UPC can also disclose the manufacturer using tools like Verified by GS1. Leading brands like Samsung, Apple, etc. provide serial number checkers to make this method more reliable for software, appliances, and electronics.
Third-party lookup tools
Third-party barcode databases offer built-in lookup features. Users can search by codes like EAN, UPC, or ISBN through their websites or order history.
Tools like Barcode Lookup retrieve data from such platforms to reveal product names, prices, and images. As a result, users can verify listings, detect errors, and compare prices.
Some third-party barcode lookup tools provide mobile scanning apps, allowing users to simply scan a product’s barcode with their smartphone, eliminating the need to manually enter the code. These apps instantly retrieve product details from extensive online databases.
Conclusion
Product code serves as the backbone of commerce, allowing businesses to track inventory, streamline operations, and ensure accurate product identification across global markets. Selecting the right code system and carrier can significantly affect your business’s efficiency and scalability.
With tools like Verified by GS1, businesses can confidently validate their GTINs and maintain data integrity. Understanding and implementing these codes isn’t just a technical necessity, it helps businesses run smoothly and grow.
FAQs
What is the difference between product codes and barcodes?
Product codes are unique product numbers that identify specific items. There are different types such as SKU and UPC. These codes help businesses track inventory, manage pricing, and distinguish between different products or variations (like size or color).
Barcodes are visual symbols that represent these codes in a machine-readable format. They come with a series of black and white lines (or patterns like QR codes) that can be scanned to quickly retrieve the product’s information from a database.
For instance, GS1 standards ensure that a GTIN is encoded into a barcode format so it can be scanned globally and thus improve data accuracy and speed in supply chains.
Can I create my product label codes?
Yes, you can make your own, but it depends on where they will be used.
For internal use (like in a warehouse or a store), you can create custom SKUs or codes and convert them into barcodes with free tools. This doesn’t need registration with an external organization.
For selling in global markets or on platforms like Amazon, you would need official codes GTINs. These should be licensed from GS1 to ensure the authenticity and uniqueness of codes globally.
How do I know if product label codes are valid?
To check validity of these codes, the most accurate and trusted method is to use Verified by GS1, a global database that validates a code’s legitimacy and links it to verified brand information.
You can search using a GTIN or company name, and if the code is authentic, you’ll see a GS1 confirmation. This not only supports supply chain transparency but also helps brands and retailers prevent errors, duplicates, and counterfeits.
DISCLAIMER: We acknowledge that GS1, as well as the materials, proprietary items, and all related patents, copyright, trademark, and other intellectual property (collectively, “intellectual property”) relating to its use, are the property of GS1 Global, and that our use of the same shall be in accordance with the conditions provided by GS1 Global.




