Value Chain vs. Supply Chain: How GS1 QR Codes Improve Both
Supply chains and value chains are connected, but they focus on different purposes. When exploring the value chain vs. supply chain, the distinction becomes clear. The supply chain handles how goods move from start to finish, while the value chain includes the supply chain and all other activities that add value to the product or service.
Understanding this connection helps businesses spot inefficiencies, manage costs, and make decisions that improve outcomes for customers.
In this setup, tools like GS1 Digital Link QR codes can work with both chains. In the supply chain, they help track products and keep inventory accurate. In the value chain, they share useful information with partners or customers, making processes more transparent. They help each chain work better.
This blog compares the supply chain vs value chain in detail, explains where they intersect, and shows where these QR codes fit.
Table of Contents
What is a supply chain?
The supply chain is the system involved in producing and delivering a product, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and final distribution. It’s more than just logistics. It’s about making sure every step works together so products arrive where they’re needed, when they’re needed, and in good condition.
Think of it like this: the supply chain is the “how” the product gets made and delivered.
Key components of a supply chain
Typically, a supply chain includes:
Procurement: Getting the raw materials or components required to manufacture a product. It involves buying these items from suppliers.
Manufacturing: Converting inputs into finished products. It’s where the actual making or assembling happens.
Warehousing: Storing goods before distribution.
Transportation: Moving goods across locations. Ships, trucks, or planes carry items between factories, warehouses, and stores.
Distribution: Delivering products to retailers or customers. This step ensures items reach the final destination, whether it’s a store shelf or a person’s doorstep.
Returns and reverse logistics: Handling defective or end-of-life products.
All components of a supply chain must work together smoothly to avoid delays, save money, and maintain product quality.
Importance of tracing the product
Traceability is the ability to follow a product through the supply chain in both directions. It allows businesses to trace materials back to their source and track products forward to their final destination. This includes the origin of inputs, processing steps, and distribution history.
Safety and recalls: Quickly identify and remove defective or unsafe products from the market.
Regulatory compliance: Meet laws and standards in industries like food, pharma, and electronics.
Quality control: Spot where errors or defects occur and fix them efficiently.
Supplier accountability: Track raw materials back to their source and ensure standards are met.
Transparency for customers: Making sourcing and handling information available when shared externally.
Inventory management: Better visibility into stock movement and location reduces losses.
Fraud prevention: Helps detect counterfeits or unauthorized substitutions.
What is the value chain?
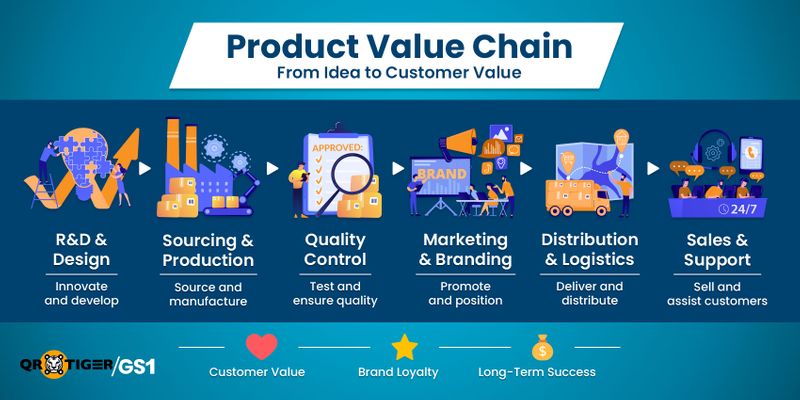
The value chain is a broad term that includes the supply chain and everything else that adds value to a product or service, from making it to delivering it and supporting customers.
It’s more than just production and logistics. It includes anything that improves the product, helps customers, or makes the business stronger.
Think of it like this: The value chain is the “why” each step matters in creating value for the customer and business.
What counts as adding value?
The product or service works correctly and does what it’s supposed to.
Extra features or improvements beyond the main function.
Better materials or ingredients, including ethically or sustainably sourced ones.
Processes that improve quality, reliability, or efficiency.
Services like support, warranties, or fast delivery.
Marketing, branding, and packaging that make the product more appealing.
Importance of tracing value
Tracing value means keeping track of what makes a product good. It’s about checking and proving each step that adds quality or appeal. This matters because:
Identify value: See which activities add real value to the product or service.
Spot inefficiencies: Find steps that waste time, money, or resources.
Better decisions: Understand costs and benefits at each stage
Drive improvement: Discover opportunities to innovate or enhance value.
Value Chain vs. Supply Chain Comparison
Feature | Supply Chain | Value Chain |
Main Goal | Efficiency & Cost Reduction | Competitive Advantage & Value Addition |
Focus | Logistics & Operations | Strategy & Innovation |
Starting Point | Sourcing raw materials | Customer needs and desires |
Ends With | Delivery of product | Customer satisfaction/loyalty |
What are GS1 Digital Link QR codes?

A GS1 Digital Link QR code is a type of 2D barcode that encodes GS1 identifiers, such as Global Trade Item Number (GTIN), batch numbers, or expiry dates, into a web-friendly format. This connects physical products directly to digital content.
Unlike traditional barcodes, these QR codes allow retailers, consumers, and supply chain partners to promptly access product details (such as ingredients, usage instructions, certifications, and traceability data) by scanning with a smartphone or point of sale (POS) system. They serve as digital gateways to detailed product information.
Businesses can generate these codes on their own by using their resources and following GS1’s implementation guidelines. Alternatively, they can use a reliable third-party service like the GS1 QR code generator to encode product data using GS1 formats.
How GS1 QR codes improve the value chain?
GS1 Digital Link QR code transforms how businesses deliver value across the product lifecycle. It helps brands offer more than just what is on the label.
Key ways these QR codes enhance the value chain
Customer engagement: GS1 QR code allows consumers to access product details, expiry date, sustainability claims, usage tips, and nutritional data. This will build trust and strengthens brand loyalty.
Transparency and authenticity: By linking to verified data sources, brands can prove claims like organic certification, cruelty-free testing, or ethical sourcing. This helps meet rising consumer expectations for detailed and authentic information on products.
Marketing and personalization: Brands can use these codes to share personalized promotions, rewards, or educational content based on where and how people scan them. This makes the product more interactive.
After-sales support: Access to troubleshooting guides, service manuals, or warranty registration adds value post-purchase.
For example, a skincare brand using Digital Link QR codes can let customers scan a product to check where ingredients come from, safety approvals, tips based on skin type, sustainability practices, and promotional offers or videos. This makes the shopping experience better and helps the brand stand out, an important goal of the value chain.
How do GS1 QR codes improve the supply chain?
Modern supply chains involve many steps, so businesses need tools to track them effectively. These QR codes do just that.
These next-generation barcodes encode GS1 identifiers, such as GTIN, SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code), and GLN (Global Location Number), in a format that connects physical products to digital data across the whole supply chain.
Key ways these codes enhance the supply chain:
Improved traceability and visibility: Digital Link QR codes help companies follow a product’s journey from start to finish. This makes it easier to spot delays, stop fake products, and act fast during recalls.
Easy data sharing: The GS1 Digital Link standard enables smooth sharing of product information across systems and partners. A single code can encode multiple data points, such as batch numbers, expiry dates, and location codes.
Reduced errors: These codes reveal details in a single scan, cutting down errors and speeding up warehouse operations, shipping, and receiving processes.
Supports regulatory compliance: Industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and logistics face strict labeling and traceability requirements. QR codes powered by GS1 help meet these by providing access to detailed product data.
For example, company shipping electronics across countries can use these QR codes to scan each unit for serial numbers, production dates, and destinations. Logistics teams get instant access to handling and customs info, whereas retailers can verify authenticity and shelf life. This improves accuracy, speeds up processes, and strengthens the supply chain overall.
 How Value and Supply Chains Work Together
How Value and Supply Chains Work Together
The value chain vs. supply chain comparison shows that each has a different role, but they work together. The supply chain makes sure products are sourced, made, and delivered correctly and on time. The value chain focuses on giving customers more value, improving their experience, building trust, and creating long-term benefits.
Every supply chain decision, from sourcing materials to moving products, affects the value customers get. At the same time, value chain goals like transparency, personalization, helpful content, and ethical sourcing can influence how the supply chain works.
Digital Link QR codes connect both chains by linking physical products to digital information. In the supply chain, they help track products, manage inventory, and handle recalls. In the value chain, they improve customer engagement, transparency, and personalized experiences, without replacing either chain.
FAQs
1. Are the value chain and the supply chain interchangeable?
No, they’re not the same, but they work together. The supply chain handles how products move from raw materials to delivery, focusing on speed, cost, and logistics.
The value chain includes all activities that make the product more useful or appealing to customers, like design, marketing, customer service, and sustainability. While the supply chain shows how a product reaches the customer, the value chain explains why it matters. In fact, the supply chain is a subset of the broader value chain.
2. How do QR codes powered by GS1 improve product traceability in the supply chain?
These codes enhance supply chain transparency by encoding multiple data elements (such as batch numbers, expiry dates, and serial numbers) into a single scannable symbol. This allows stakeholders across the supply chain to track a product’s journey from origin to destination, improving inventory accuracy, recall management, and regulatory compliance.
3. How do QR codes powered by GS1 support both supply chain efficiency and value chain transparency?
In the supply chain, these codes help track products, follow rules, and move goods smoothly. In the value chain, they provide clear product info, build customer trust, and improve customer experience. By embedding all key data into one smart code, businesses can optimize backend processes while enriching front-end experiences.
DISCLAIMER: We acknowledge that GS1, as well as the materials, proprietary items, and all related patents, copyright, trademark, and other intellectual property (collectively, “intellectual property”) relating to its use, are the property of GS1 Global, and that our use of the same shall be in accordance with the conditions provided by GS1 Global.



